Delivering consistent quality is essential for building brand reputation and customer loyalty. To achieve this, businesses rely on proven techniques known as quality control tools. These tools help identify problems, monitor progress, and maintain standards throughout the production or service process.
Understanding Quality Control Tools
Quality control tools are practical techniques used to analyze, manage, and improve quality in a systematic way. They are essential for identifying errors, improving processes, and ensuring that the final output meets required specifications.
Across various industries, teams use Quality Control Tools to collect accurate data, evaluate process behavior, and spot variations that may lead to defects. These tools make it easier to detect issues early and take corrective action, reducing the risk of major failures or costly rework.
Role of Quality Control Tools in Business
Integrating Quality Control Tools into business operations enhances efficiency, reduces waste, and supports a culture of continuous improvement. These tools are especially helpful in manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and other sectors where precision and consistency are critical.
They empower decision-makers by turning raw data into visual insights, making problem-solving more effective. When used correctly, these tools can significantly boost product reliability and customer satisfaction.
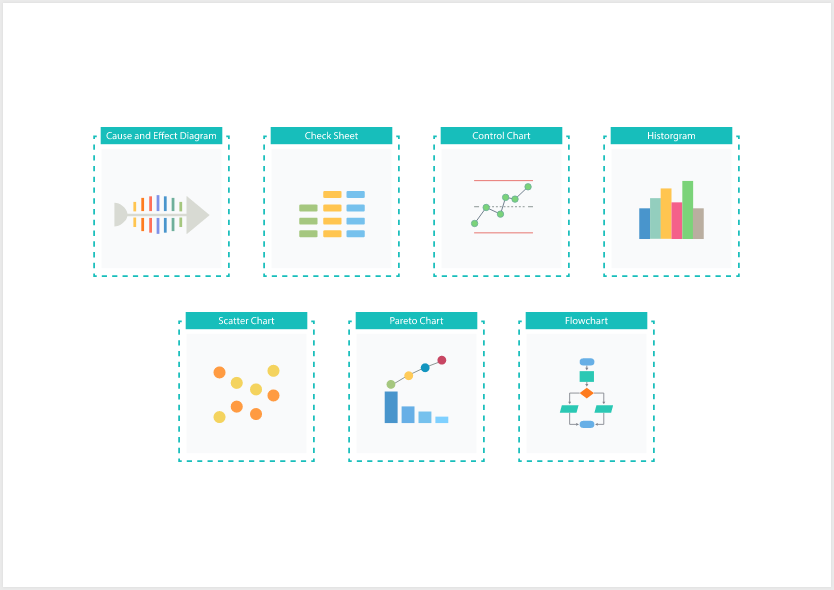
The Seven Basic Quality Control Tools
Here are the seven most commonly used tools that form the foundation of quality control practices:
- Cause-and-Effect Diagram (Ishikawa/Fishbone Diagram)
Identifies possible causes of a problem and categorizes them for further analysis. - Check Sheet
A simple, structured form for collecting and analyzing data in real time. - Control Chart
Tracks process variations over time to determine if the process is under control. - Histogram
Provides a graphical representation of data distribution and variability. - Pareto Chart
Helps prioritize issues by showing which problems are most frequent or impactful. - Scatter Diagram
Displays the relationship between two variables to identify possible correlations. - Flow Chart
Visualizes the steps in a process, making it easier to identify bottlenecks or unnecessary steps.
Tips for Effective Use of Quality Control Tools
- Choose the right tool for the problem you are addressing
- Ensure data is accurate and collected consistently
- Involve cross-functional teams for broader insights
- Use visuals to communicate findings and drive action
Conclusion
Quality control tools are essential for businesses committed to excellence. They offer a structured way to evaluate performance, solve problems, and improve outcomes. By mastering these tools, companies can ensure quality at every level, reduce inefficiencies, and build lasting trust with customers.
The Seven Basic Quality Control Tools
Here are the seven most commonly used tools that form the foundation of quality control practices:
- Cause-and-Effect Diagram (Ishikawa/Fishbone Diagram)
Identifies possible causes of a problem and categorizes them for further analysis. - Check Sheet
A simple, structured form for collecting and analyzing data in real time. - Control Chart
Tracks process variations over time to determine if the process is under control. - Histogram
Provides a graphical representation of data distribution and variability. - Pareto Chart
Helps prioritize issues by showing which problems are most frequent or impactful. - Scatter Diagram
Displays the relationship between two variables to identify possible correlations. - Flow Chart
Visualizes the steps in a process, making it easier to identify bottlenecks or unnecessary steps.
Tips for Effective Use of Quality Control Tools
- Choose the right tool for the problem you are addressing
- Ensure data is accurate and collected consistently
- Involve cross-functional teams for broader insights
- Use visuals to communicate findings and drive action
Conclusion
Quality control tools are essential for businesses committed to excellence. They offer a structured way to evaluate performance, solve problems, and improve outcomes. By mastering these tools, companies can ensure quality at every level, reduce inefficiencies, and build lasting trust with customers.